Foreword
This is an individual master’s degree project. Although the topic “Procedural Generation” is supposed to be strongly related to computer graphics, this project focuses more on the plant distribution algorithm rather than deep diving into operations on vertices or textures. But, I still regard this project as my solid step into the computer graphics area and video game industry. I would be glad if you find the project useful or inspiring!
Problem Statement
Current procedural generation systems pay more attention to pure nature terrain or city buildings, and small forests like parks or neighborhoods are seldom considered. So this project will be focusing on procedurally generating small-scale urban forests. The goal is to design a system that takes a satellite map image and generates forest in the tree areas in the image.
Concept Generation
The system structure overview is shown in the following image.
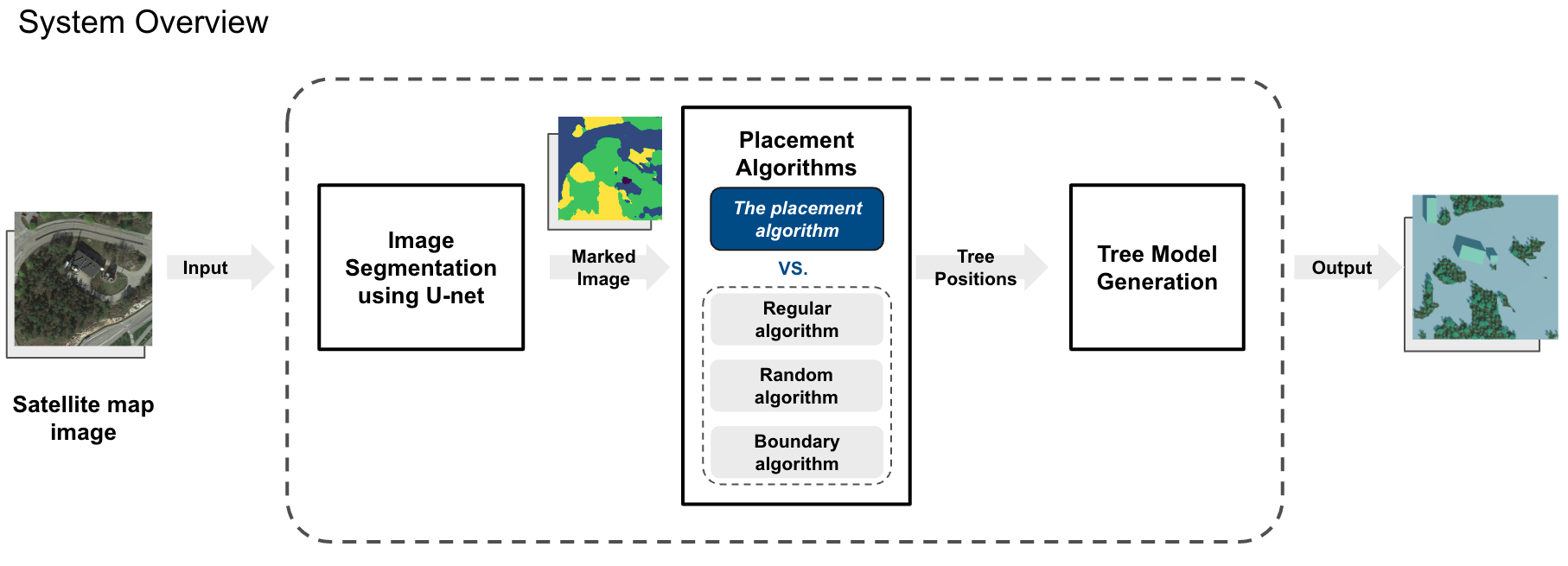
The input of the system is a satellite map image. The first module of the system is to segment the map image using a machine-learning model. It will mark the tree area in the image. Then the second module is the core of the system. This module can deploy certain algorithms to generate tree positions in the marked areas. The algorithm used here will determine the distribution of trees in the forest, and thus affects the realism of the scene. The last module is to generate tree models at the positions calculated in the last module.
Design Description
The first module uses the U-net model written in Python. The input and the results are shown in the right images. The training dataset is open source and small-scale. This U-net tutorial helped me a lot in implementing this module. The inputs and outputs are shown in the image below:

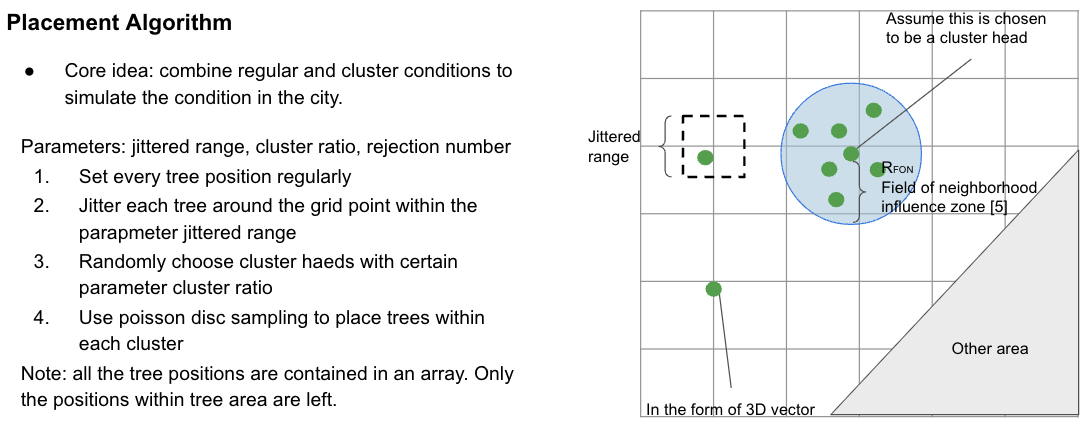
As for the second module, the core idea of the algorithm is to combine regular and cluster conditions to simulate the condition in the city. The adjustable parameters are jittered range, cluster ratio, and rejection number. The placement algorithm starts by setting every tree position regularly. After that, it jitters each tree around the grid point within the parameter jittered range. Then some trees are randomly chosen as the cluster heads with the parameter cluster ratio. In the end, the algorithm uses Poisson disc sampling to place trees within each cluster. The parameter rejection number limits the number of trees within a cluster. Notice that each position will be checked and only the positions within the tree area are left. And all the tree positions are contained in an array data structure.
As for the tree model generation, I used the same implementation from Procedural generation of imaginative trees using a space colonization algorithm for tree model generation. Tree models are generated at each position. Each tree model has a similar shape but is distinct. An example is shown in the right image.
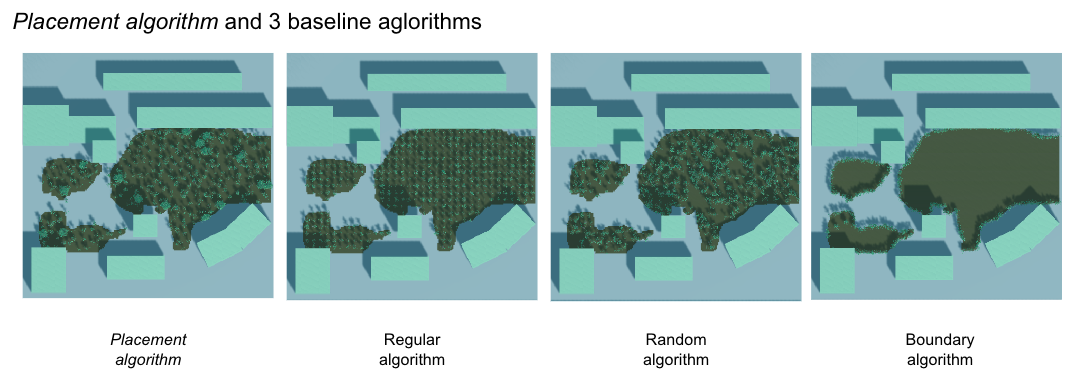
As for the thesis project, there is actually almost half of the workload comes from the user evaluation to compare to baseline algorithms. However, this part is tedious and most not related to technology. The example results are shown below: