Modern Game Engine Course Notes 01
Course from: BoomingTech
Introduction
What’s Game Engine? Definition from the course:
- Technology foundation of the Matrix
- Productivity tools of creation
- The Art of complexity
Layered Architecture of Game Engine
Simplified game engine structure:
- Tool Layer: tools in the editor
- Function Layer: animation, physics, rendering, camera, HUB and Input, script, FSM and AI
- Resource Layer: Scene and Level, Script and Graph, Game Logic Data
- Core Layer: container, memory management, thread pool, math
- Platform Layer: operation systems, platform file system, graphics API, platform SDK, etc..
- Third Party Libraries: TrueSky, SpeedTree, etc..
Resource
Unify file access by defining a meta asset file format (ie.ast). Assets are faster to access by importing preprocess. Build a composite asset file to refer to all resources. GUID is an extra protection of reference.
Runtime Resource Management: A virtual file system to load/unload assets by path reference. Manage asset lifespan and reference by handle system.
Memory management for Resources - life cycle:
- Different resources have different life cycles.
- Limited memory requires release of loaded resources when possible.
- Garbage collection and deferred loading is critical features.
Function
A tick function to run the entire world within a unit of time. In tickMain, we run tickLogic and tickRender to describe how the world runs and looks.
Function Layer provides major function modules for the game engine: Object system (HUGE).
Game Loop updates the systems periodically: Game Loop is the key of reading codes of game engines.
Blur the boundary between engine and game: Camera, character and behavior; Design extendable engine API for programmer.
Multi-core processors become the mainstream: Many systems in game engine are built for parallelism.
Core
Math library: Linear algebra. The efficiency of the used functions matters very much.
Data structure and containers like vectors, maps, etc. It requires customized that outperform STL.
Memory management: the major bottlenecks of game engine performance is limited by memory pool, reducing cache miss, memory alignment. Polymorphic memory resource (PMR):
- Put data together
- Access data in order
- Allocate and de-allocate as a block
Platform
Compatibility of different platforms, provides platform-independent services and information for upper layers: File system, Path: Slash/backslash, Environment variables, Directory Traversal.
Render Hardware Interface (RHI): Transparent different GPU architectures and SDK, Automatic optimization of target platforms.
Tool
Unleash the Creativity:
- Build upon game engine.
- Create, edit and exchange game play assets (level editor, shader editor, logical editor, etc.).
Flexible of coding languages: C++, C#, HTML and CSS, etc.
How to Build a Game World
Dynamic game object
Static game object
Environments: sky, vegetation, terrain
Other game objects: air wall, trigger area, navigation mesh, etc.
Game Object (GO) is the abstraction of almost everything in the game world.
Game object:
- Property
- Behavior
- Inheritance
There are problem problems with inheritance
Base game object on components.
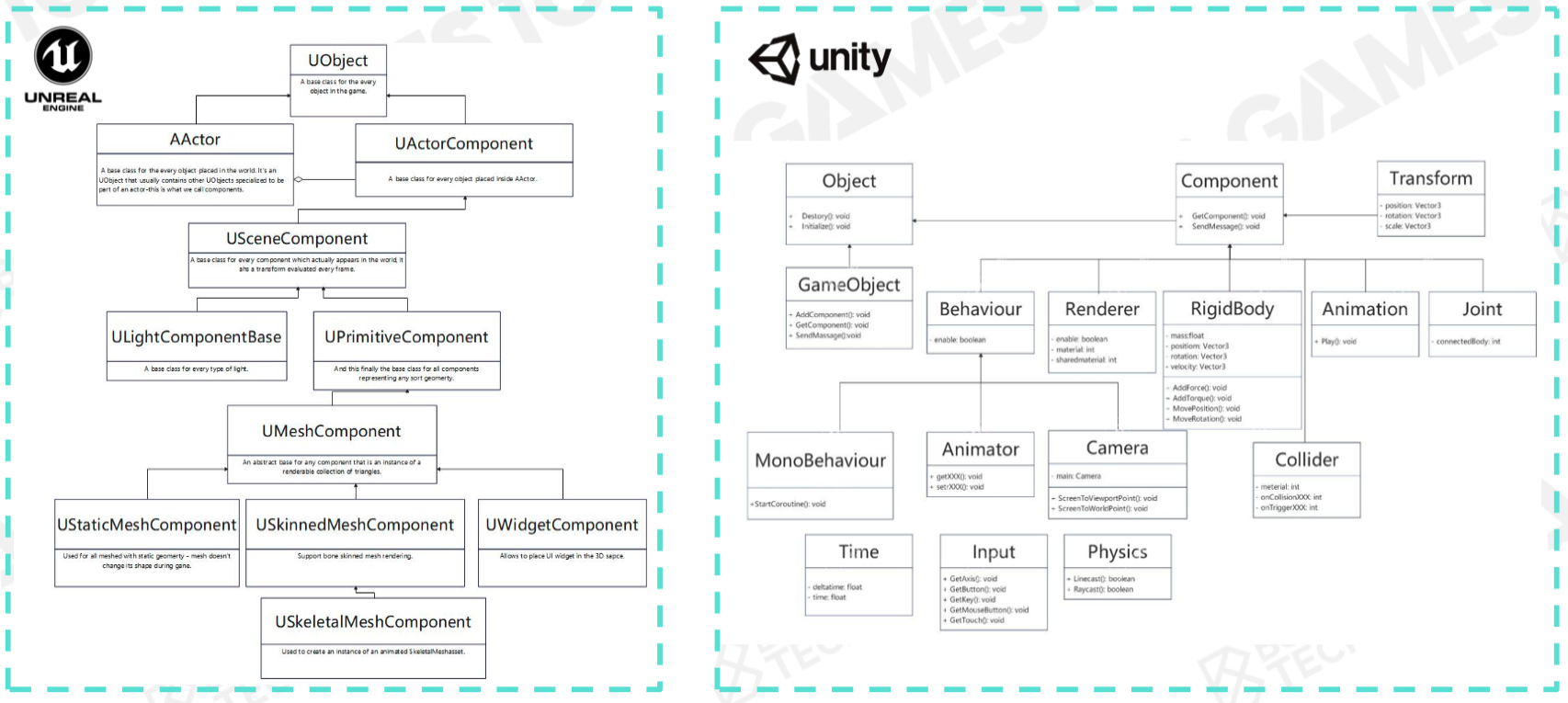
Object-based Tick (Intuitive)
Component-based Tick (Parallelized processing, reduce cache miss)
Events
- Message sending and handling
- Decoupling event sending and handling
Scene Management
- Game objects are managed in a scene
- Game object query
- By unique game object ID
- By object position
- Hierarchical segmentation: bounding volume hierarchies (BVH), octree, binary space partitioning (BSP), etc.
Takeaways:
- Everything is an object
- Game object could be described in the component-based way - States of game objects are updated in tick loops
- Game objects interact with each other via event mechanism
- Game objects are managed in a scene with efficient strategies